DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is a security extension to the DNS protocol. It protects against DNS manipulation by adding digital signatures to DNS responses, allowing users to verify that the information they receive is authentic and has not been tampered with. This prevents attackers from redirecting users to fake websites.
How does DNSSEC work?
Standard DNS is not encrypted or signed, making it vulnerable to DNS spoofing or cache poisoning attacks. DNSSEC addresses this by signing DNS records with cryptographic keys.
When a user requests a domain:
- The DNS resolver checks whether the response contains a valid DNSSEC signature.
- It validates this signature using a chain of trust with public keys from higher-level DNS zones.
- Only verified responses are accepted and passed on.
This significantly reduces the risk of users being unknowingly redirected to malicious servers.
Why is DNSSEC important?
DNSSEC protects one of the most critical parts of internet infrastructure. It helps:
- Prevent man-in-the-middle attacks via DNS.
- Build trust in web services and digital communications.
- Comply with regulations like NIS2 or the Dutch BIO, which explicitly recommend or require DNSSEC.
Despite its benefits, DNSSEC adoption remains inconsistent. It requires technical implementation and ongoing validation, as misconfigured DNSSEC can block legitimate traffic.
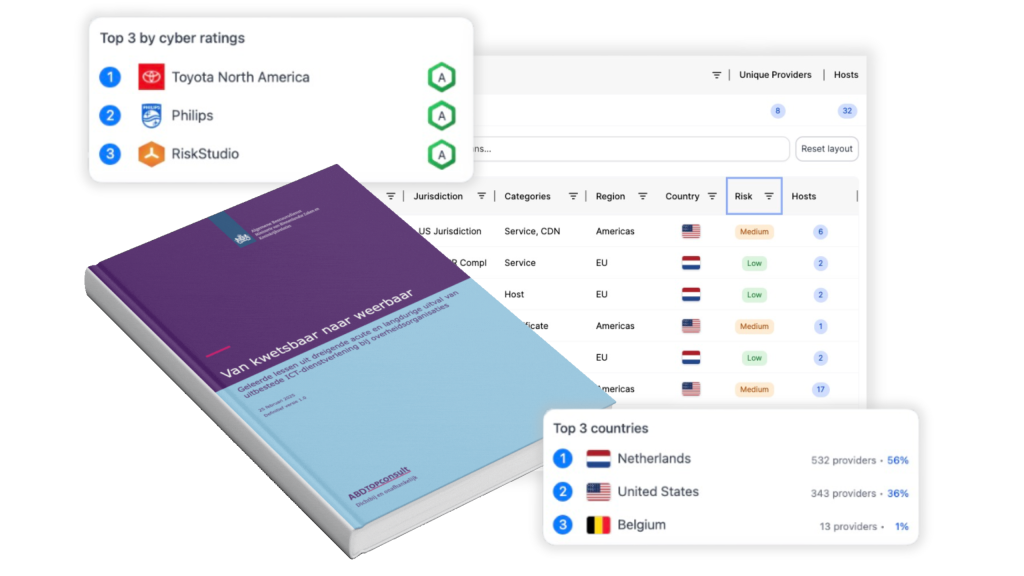
DNSSEC and RiskStudio
RiskStudio helps you evaluate the DNS security of your suppliers — including whether DNSSEC is in place and correctly configured. Our platform automatically checks DNSSEC signatures, validates trust chains, and alerts you when records are missing, invalid, or expired. This allows you to reduce risk across your supply chain and ensure your partners don’t become a weak link in your cybersecurity efforts.